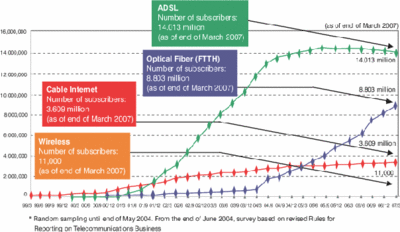
 Japanese broadband uptake as of March 2007:
Japanese broadband uptake as of March 2007:
| 14.013 million | aDSL |
| 8.803 million | FTTH |
| 3.609 million | Cable |
| 11 thousand | Wireless |
As of March 2007, merely 95% of all Japanese households had broadband, and 84% had ultra-highspeed broadband. Japanese government goals for 2010 are 100% and 90%, respectively. Ultra-highspeed seems to be defined as both up and down over 30Mbps.
Until now, FTTH has been the mainstream in terms of ultra-highspeed broadband, with upload and download speeds of over 30Mbps, but other wired and wireless technologies are aiming for technologies that will match if not overtake FTTH, and there will be a need for ongoing developments in broadband technology in terms of higher speed and larger volume to meet user needs.Higher speed services in testing now include speeds faster than 1 Gbps, which would be around 300 times faster than what passes for broadband in the U.S. Continue reading— Study Group Report: Moving towards Establishing a Usage Environment for Next-Generation Broadband Technology, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications (MIC), MIC Communications News, Vol. 18, No.13, 12 October 2007




 In the
In the
 Monopolies sometimes come in small sizes:
Monopolies sometimes come in small sizes: