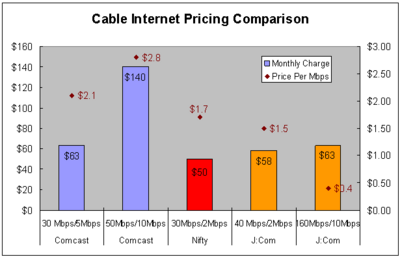
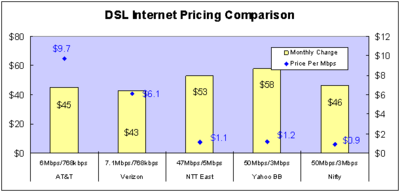
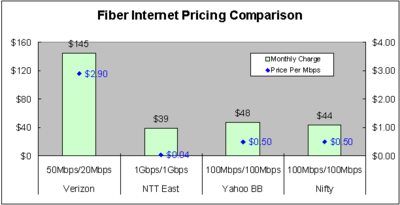
Wozniak to the FCC on net neutrality:
Wozniak to the FCC on net neutrality:
Imagine that when we started Apple we set things up so that we could charge purchasers of our computers by the number of bits they use. The personal computer revolution would have been delayed a decade or more. If I had to pay for each bit I used on my 6502 microprocessor, I would not have been able to build my own computers anyway.He also details examples of how difficult it was to start a new service the way the telephone system used to be, how radio used to all be freely receivable, and how cable TV is mis-regulated. He summarizes his case:
I frequently speak to different types of audiences all over the country. When I’m asked my feeling on Net Neutrality I tell the open truth. When I was first asked to “sign on” with some good people interested in Net Neutrality my initial thought was that the economic system works better with tiered pricing for various customers. On the other hand, I’m a founder of the EFF and I care a lot about individuals and their own importance. Finally, the thought hit me that every time and in every way that the telecommunications careers have had power or control, we the people wind up getting screwed. Every audience that I speak this statement and phrase to bursts into applause.Then he asks for all that not to happen to the Internet:
We have very few government agencies that the populace views as looking out for them, the people. The FCC is one of these agencies that is still wearing a white hat. Not only is current action on Net Neutrality one of the most important times ever for the FCC, it’s probably the most momentous and watched action of any government agency in memorable times in terms of setting our perception of whether the government represents the wealthy powers or the average citizen, of whether the government is good or is bad. This decision is important far beyond the domain of the FCC itself.Ain’t that the truth.
-jsq