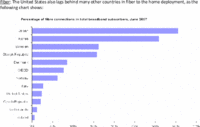
The figure shows new applications becoming possible as speeds increase,
starting with electronic mail at the lowest speeds, through VoIP, also
at a pretty low speed, and on up through multi-player games, video on
demand, virtual reality, and telepresence.
A few big ones seem to be missing, such as file transfer and the
world wide web, but maybe those were available at too low speeds
to mention.
This point of speed enabling new applications is important, but
even more so is what people do with those applications.
As Sharon Strover says, perhaps we should frame the discussion more in
terms of competencies, rather than speeds.
Or, as IIA says:
Business use of video conferencing is expected to increase as rising fuel
prices, business continuity planning for possible avian flu pandemic or
terrorist attack, environmental concerns and the provision of greater
work/life balance for employees, begin to build pressure for workforce
decentralisation. The Australian Telework Advisory Committee in its final
report also recognised the productivity benefits that teleworking can
deliver to business.11 These factors will see businesses require more
broadband capacity and performance.
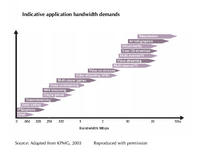
Overall, we anticipate that users will demand a mix of simultaneous
or near simultaneous services to be accessible. As a guide, we would
expect access services to be able to support concurrent uses of some or
all of the following VoIP, gaming, multichannel streaming and video on
demand (including HDTV quality), music, legitimate P2P file sharing,
and browsing. The figure below illustrates the individual bandwidth
requirements for a range of services.
—
2010 National Broadband Targets: Maintaining Australia’s Competitiveness,
p. 10-11,
Internet Industry Association,
31 July 2006
Notice that many of these applications are participatory, and more
intensely vivid methods of participations such as telepresence
become available at higher speeds.
However, electronic mail (one-to-one communication), mailing lists
(one-to-many) and USENET newsgroups (many-to-many) were participatory
at speeds most users would sniff at these days.
Yet it takes higher speeds to do graphically-oriented multi-user
roleplaying games such as World of Warcraft.
Such games have hordes of paying users, especially in countries such
as Korea with high access speeds.
Participation breeds revenue, which fuels speed.
Business and recreation aren’t the only uses of participation.
Continue reading →
 This is amusing:
This is amusing: