 Creeping ahead:
Creeping ahead:
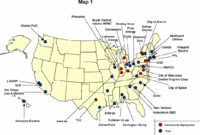
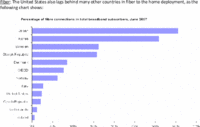
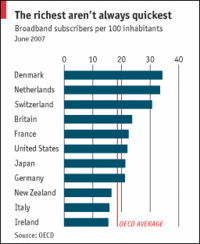
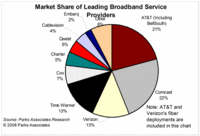
A study from Texas-based research firm Parks Associates predicts that 33 million US households will have broadband connections of 10Mbps or faster by 2012. As of the end of 2007, that figure stood at 5.7 million, which means that a lot of change will have to occur in the US market for that 33 million figure to become a reality.Meanwhile, Japan is already doing 100Mbps. But in Japan there is real ISP competition. Unlike in the U.S., where, as shown in the pie chart by Park Associates (via DSL Reports), each of Comcast and AT&T have a fifth of the broadband market, followed by Verizon and Time Warner each with 13%, plus Cox with 7%, and that’s 3/4 of the total market served by only five companies, of whom most people have a choice of only two in any given locality. That’s not competition.— Report: 10Mbps broadband in 33 million homes by 2012, By Eric Bangeman, ars technica, Published: March 04, 2008 – 10:20PM CT
-jsq