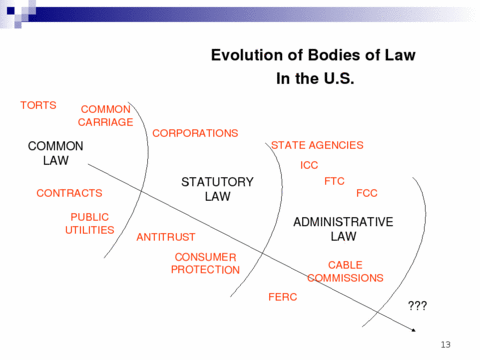
At TPRC Sunday, Barbara Cherry walked through the evolution of bodies of law
in the U.S., and made some fascinating observations, including:
-
Net neutrality is a manifestation of moving from a Title II industry-specific
business legal regime under the Communications Act of 1934 to a Title I
I-based regime and greater reliance on a general business regime of antitrust and consumer protection laws, as
the FCC did in August 2005 for wireline broadband access service to the Internet and in 2002 for cable modem access service.
-
Simply mMoving among traditional and deregulatory legal regimes for transportation carriers does did not strip common carriage status;
it merely changesd the legal overlay that enforcesd it.
-
FCC stripping broadband of common carriage was a radical departure:
nothing classified as common carrier has ever been declassified before.
-
Anti-trust doesn’t automatically cover problems
from previously addressed in the Title II industry-specific regime
when a business is moved to the Title II general business regime.
Anti-trust needs modification to do this.
-
Liability is also different between regimes.
Without tariffs some legal protections for limited liability
constraints are gone, and common carriers are now
potentially fully liable for damages.
The final filed rate doctrine should have no applicability to a detariffed world.
The above is, I think, a reasonably close paraphrase of some of her points.
I infer from this that the economists and politicians and telco and cableco
executives who say that we shouldn’t regulate because we don’t know what
will happen and anti-trust will catch problems if they occur are not
taking into account that anti-trust doesn’t automatically apply to or address problems in the new legal regime into which broadband has been thrust.
In other words, people see things in the context of what they know,
and economists don’t usually know about legal evolution.
Telco and cableco executives, on the other hand, may well have business
and political reasons for claiming there’s no need for regulation,
whether or not they know that existing anti-trust law is inadequate. doesn’t apply.
You can’t have markets without some form of property rights
of contract law.
There is also basic legal infrastructure you need
for communication infrastructure.
I see little or no understanding of these points in FCC, FTC, or Congress.
Prof. Cherry’s whole paper is well worth reading:
Consumer Sovereignty: Redrawing the Boundaries Between Industry-Specific and General Business Legal Regimes for Telecommunications and Broadband Access Services,
by Barbara A. Cherry,
TPRC,
30 Sep 2007
-jsq
PS: Markup for increased accuracy kindly supplied by Prof. Cherry.
 Cringely claims credit for wireless craze:
Cringely claims credit for wireless craze: